- Часовые пояса Канады
- Содержание
- Часть, расположенная а часовом поясе UTC-8
- Часть, расположенная а часовом поясе UTC-7
- Часть, расположенная а часовом поясе UTC-6
- Часть, расположенная а часовом поясе UTC-5
- Часть, расположенная а часовом поясе UTC-4
- Часть, расположенная а часовом поясе UTC-3:30
- Смотреть что такое «Часовые пояса Канады» в других словарях:
- Введение часовых поясов и летнего времени в Канада
- Временные зоны в настоящее время используется в Канада
- Временные зоны, которые будут использоваться в Канада
- Time in Canada
- Contents
- Official time [ edit ]
- Time notation [ edit ]
- Zones [ edit ]
- Pacific Time Zone [ edit ]
- Mountain Time Zone [ edit ]
- Central Time Zone [ edit ]
- Eastern Time Zone [ edit ]
- Atlantic Time Zone [ edit ]
- Newfoundland Time Zone [ edit ]
- Former time zones [ edit ]
- Daylight saving time [ edit ]
Часовые пояса Канады
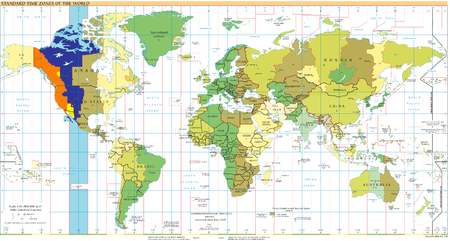
Территория Канады располагается в шести часовых поясах: Североамериканское тихоокеанское время (UTC−8), Горное время (UTC−7), Центральное время (UTC−6), Североамериканское восточное время (UTC−5), Атлантическое время (UTC−4) и UTC−3:30. Некоторые части страны переходят на летнее время и оказываются в часовых поясах UTC−3 и UTC−2:30.
Содержание
Часть, расположенная а часовом поясе UTC-8
- В течение всего года
Северо-Западные территории:
- Посёлок Тунгстен
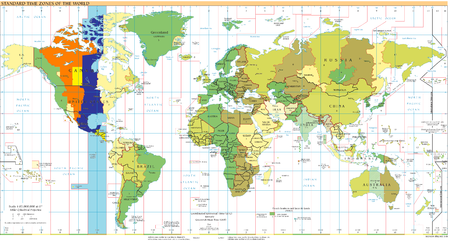
Часть, расположенная а часовом поясе UTC-7
- В течение всего года:
Британская Колумбия:
- Часть долинырекиПис-Ривер
- Зимой:
Альберта
Британская Колумбия (юго-восточная часть)
Нунавут (западная часть)
Саскачеван (только городЛлойдминстер и прилегающий район)
Северо-Западные территории (большая часть)
- Летом:
Британская Колумбия (большая часть)
Юкон
Часть, расположенная а часовом поясе UTC-6
- Зимой:
Манитоба
Нунавут (центральная часть)
Онтарио (западная часть)
- Летом:
Альберта
Британская Колумбия (юго-восточная часть)
Северо-Западные территории (большая часть)
Нунавут (западная часть)
Саскачеван (только город Ллойдминстер и прилегающий район)
Часть, расположенная а часовом поясе UTC-5
- В течение всего года:
- Остров Саутгемптон
- Зимой:
Нунавут:
- Территория восточнее 85° з. д. (Восточный Нунавут)
Квебек:
- Большая часть (западнее 63° з. д.)
Онтарио:
- Большая часть (восточная)
- Летом:
Нунавут:
- Центральная часть
Манитоба
Онтарио:
- Западная часть
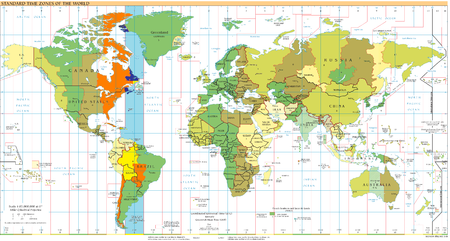
Часть, расположенная а часовом поясе UTC-4
- В течение всего года:
Квебек:
- Территория восточнее 63° з. д.
- Зимой:
Ньюфаундленд и Лабрадор:
- Большая часть региона Лабрадор
Нью-Брансуик
Остров Принца Эдуарда
Новая Шотландия
- Летом:
Нунавут:
- Территория восточнее 85° з. д. (Восточный Нунавут)
Квебек:
- Большая часть (западнее 63° з. д.)
Онтарио:
- Большая часть (восточная)
Часть, расположенная а часовом поясе UTC-3:30
| Страны Северной Америки: Часовые пояса | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Offset | Часовой пояс | Пример Город | Текущее время |
| UTC -07:00 | MST | Creston | 08:41 ВТР, 2021-04-27 |
| UTC -07:00 | PDT | Виктория Город | 08:41 ВТР, 2021-04-27 |
| UTC -06:00 | CST | ирга ольхолистная | 09:41 ВТР, 2021-04-27 |
| UTC -06:00 | MDT | Калгари | 09:41 ВТР, 2021-04-27 |
| UTC -05:00 | CDT | Виннипег | 10:41 ВТР, 2021-04-27 |
| UTC -04:00 | EDT | Торонто | 11:41 ВТР, 2021-04-27 |
| UTC -03:00 | ADT | Галифакс | 12:41 ВТР, 2021-04-27 |
| UTC -02:30 | NDT | Сент-Джонс, Ньюфаундленд и Лабрадор | 13:11 ВТР, 2021-04-27 |
Временные зоны, которые будут использоваться в Канада
Источник
Time in Canada
Time zones in Canada
| Standard | DST | Time zone |
|---|---|---|
| UTC−08:00 | UTC−07:00 | Pacific |
| UTC−07:00 (year round) | Mountain | |
| UTC−07:00 | UTC−06:00 | Mountain |
| UTC−06:00 (year round) | Central | |
| UTC−06:00 | UTC−05:00 | Central |
| UTC−05:00 (year round) | Eastern | |
| UTC−05:00 | UTC−04:00 | Eastern |
| UTC−04:00 (year round) | Atlantic | |
| UTC−04:00 | UTC−03:00 | Atlantic |
| UTC−03:30 | UTC−02:30 | Newfoundland |
Canada is divided into six time zones, based on proposals by Scottish Canadian railway engineer Sandford Fleming, who pioneered the use of the 24-hour clock, the world’s time zone system, and a standard prime meridian. [1] Most of Canada operates on standard time from the first Sunday in November to the second Sunday in March and daylight saving time the rest of the year. [2]
Contents
Official time [ edit ]
The National Research Council (NRC) maintains Canada’s official time through the use of atomic clocks. [3] The official time is specified in legislation passed by the individual provinces. In Quebec it is based on coordinated universal time. [4] The other provinces use mean solar time. [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] [10] [11] [12] [13] [14] The NRC provides both coordinated universal time and mean solar time in its signals. [15] It makes time servers available for direct synchronization with computers. The Canadian Broadcasting Corporation has aired a daily time signal, the National Research Council Time Signal, since November 5, 1939. [16]
Time notation [ edit ]
The Government of Canada recommends use of the 24-hour clock (e.g. 01:40), which is widely used in contexts such as transportation schedules, parking meters, and data transmission. [17] Speakers of Canadian French predominantly use this system, but most users of Canadian English use the 12-hour clock in everyday speech (e.g. 1:40 a.m.), even when reading from a 24-hour display, similar to the use of the 24-hour clock in the United Kingdom.
Zones [ edit ]
Pacific Time Zone [ edit ]
Pacific Standard Time (PST) GMT−08:00 and Pacific Daylight Time (PDT) GMT−07:00:
Mountain Time Zone [ edit ]
Mountain Standard Time (MST) GMT−07:00 and Mountain Daylight Time (MDT) GMT−06:00:
- Alberta
- British Columbia, southeastern
- Columbia-Shuswap Regional District east of the Selkirk Mountains
- Regional District of East Kootenay
- Regional District of Central Kootenay east of the Kootenay River and some parts east of Kootenay Lake that are south of and including Riondel (but not Creston, which is MST year round, and Kootenay Bay–Crawford Bay area, which is Pacific Daylight Time)
- Northwest Territories, except for Tungsten (see above), two fishing lodges in the southeast and a mine site in the southwest [note 1]
- Nunavut ( see Time in Nunavut )
- west of 102° West, and
- all communities in the Kitikmeot Region
- Saskatchewan (
- see Time in Saskatchewan )
- Lloydminster and surrounding area (the municipal government chose to unify the entire city with Alberta’s time zone)
Mountain Standard Time (MST) GMT−07:00 year-round:
Central Time Zone [ edit ]
Central Standard Time (CST) GMT−06:00 and Central Daylight Time CDT GMT−05:00:
- Manitoba
- Saskatchewan
- Creighton (unofficial)
- Nunavut
- between 85° West and 102° West, and
- Resolute plus all communities in the Kivalliq Region and the west shore of Hudson Bay except Southampton Island (Coral Harbour)
- Ontario, northwestern
- west of 90° West (except the Atikokan, New Osnaburgh and Pickle Lake areas, and the Shebandowan and Upsala areas)
- east of 90° West: Big Trout Lake area
Central Standard Time (CST) GMT−06:00 year-round:
- Saskatchewan (most of the province) (see Lloydminster, and Creighton, above)
Eastern Time Zone [ edit ]
Eastern Standard Time (EST) GMT−05:00 and Eastern Daylight Time (EDT) GMT−04:00:
- Nunavut
- east of 85° West, and
- all communities in the Qikiqtaaluk Region except Resolute
- Ontario
- east of 90° West (except the Big Trout Lake area), plus
- west of 90° West: Shebandowan and Upsala areas
- Quebec (most of province)
- Areas of Labrador adjacent to Schefferville (in Quebec but very close to the Labrador border) use EST and DST unofficially.
Eastern Standard Time (EST) GMT−05:00 year-round:
Atlantic Time Zone [ edit ]
Atlantic Standard Time (AST) GMT−04:00 and Atlantic Daylight Time (ADT) GMT−03:00:
Atlantic Standard Time (AST) UTC−04:00 year-round:
Newfoundland Time Zone [ edit ]
Newfoundland Standard Time (NST) GMT−03:30 and Newfoundland Daylight Time (NDT) GMT−02:30:
Former time zones [ edit ]
- The Yukon Time Zone (GMT−09:00) covered Yukon from 1900 until 1966. In 1983, the zone (then covering only a small portion of Alaska) was restructured to cover most of Alaska and renamed the Alaska Time Zone.
- In 1988, Newfoundland used «double daylight saving time» from April 3 until October 30, meaning that the time was set ahead by 2 hours. [20] All of Newfoundland and southern Labrador, which uses GMT−03:30 as its standard time zone, used GMT−01:30. [21] This only happened in 1988 and the province now only adjusts its time by one hour for daylight saving time.
Daylight saving time [ edit ]
Four Canadian cities, by local ordinance, used daylight saving time in 1916. Brandon, Manitoba, adopted it on April 17. It was followed by Winnipeg on April 23, Halifax on April 30, and Hamilton, Ontario, on June 4. [22] Port Arthur, Ontario, was the first place in the world to introduce it, on July 1, 1908.
Daylight saving time is currently observed in nine of ten provinces and two of three territories, but with exceptions in several provinces and Nunavut. Most of the province of Saskatchewan, despite geographically being in the Mountain Time Zone, observes year-round CST. In 2020, the territory of Yukon abandoned seasonal time change and moved to permanently observing MST year-round. [23] Under the Constitution of Canada, laws related to timekeeping are a purely provincial matter. In practice, since the late 1960s DST across Canada has been closely or completely synchronized with its observance in the United States to promote consistent economic and social interaction. When the United States extended DST in 1987 to the first Sunday in April, all DST-observing Canadian provinces followed suit to mimic the change.
In 2019, the legislature of British Columbia began the process of eliminating the practice of observing daylight saving time in the province. On October 31, 2019, the government introduced Bill 40 in the legislature, which would define «Pacific Time» as «7 hours behind Coordinated Universal Time (UTC)». [24] In a press release, the provincial government stated an intention to maintain alignment of clock time with Washington, Oregon, California, and Yukon. [25] The move follows a consultation earlier in 2019, in which the province received over 223,000 responses, 93% of which said they would prefer year-round DST as compared to the status quo of changing the clocks twice a year. [26] [27] [28] The premier of British Columbia discussed the issue with Yukon premier Sandy Silver, who said in October that he needs more consultation with Yukon stakeholders, and with Alberta and Alaska. [29]
The latest United States change (Energy Policy Act of 2005), adding parts of March and November starting in 2007, was adopted by the various provinces and territories on the following dates:
- Ontario [30] and Manitoba [31] – October 20, 2005
- Quebec – December 5, 2005 [32]
- Prince Edward Island – December 6, 2005 [33]
- New Brunswick – December 23, 2005 [34]
- Alberta – February 2, 2006 [35]
- Northwest Territories – March 4, 2006 [36]
- British Columbia – March 31, 2006 [37]
- Nova Scotia – April 25, 2006 [38]
- Yukon – July 14, 2006. [39] Year-round MST as of March 8, 2020. [23]
- Newfoundland and Labrador – November 20, 2006, but officially announced on January 18, 2007 [40]
- Nunavut – February 19, 2007 [41]
- Saskatchewan – No official action was taken, as almost all of the province remains on CST year-round. However, the few places in the province that do observe daylight saving (Lloydminster and the surrounding area, which straddles the Alberta border and observes Alberta’s Mountain Time – and Creighton, which observes daylight saving on an unofficial basis due to its proximity to the border with Manitoba) follow the aforementioned March–November schedule just like the rest of the country.
Источник



 Северо-Западные территории:
Северо-Западные территории: Британская Колумбия:
Британская Колумбия: Альберта
Альберта Нунавут (западная часть)
Нунавут (западная часть) Саскачеван (только городЛлойдминстер и прилегающий район)
Саскачеван (только городЛлойдминстер и прилегающий район) Юкон
Юкон Манитоба
Манитоба Онтарио (западная часть)
Онтарио (западная часть) Квебек:
Квебек: Ньюфаундленд и Лабрадор:
Ньюфаундленд и Лабрадор: Нью-Брансуик
Нью-Брансуик Остров Принца Эдуарда
Остров Принца Эдуарда Новая Шотландия
Новая Шотландия



